Understanding LiFePO4 Batteries: A Quick Guide to Lithium Iron Phosphate Fundamentals
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries, often simply called "Iron Lithium batteries," are a prominent type of lithium-ion battery. They've gained significant attention for their high safety, long cycle life, and excellent stability, making them widely used in electric vehicles, energy storage systems, and various other applications.
1. LiFePO4 Batteries Structure
- Cathode Material: LFP batteries use Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO4) as their cathode material. This material offers a stable discharge platform and superior structural stability.
- Anode Material: Graphite is typically employed as the anode material.
- Electrolyte: The electrolyte usually consists of organic solvents containing lithium salts.
- Separator: A separator prevents direct contact between the cathode and anode, ensuring safe battery operation.
2. How They Work (Working Principle)
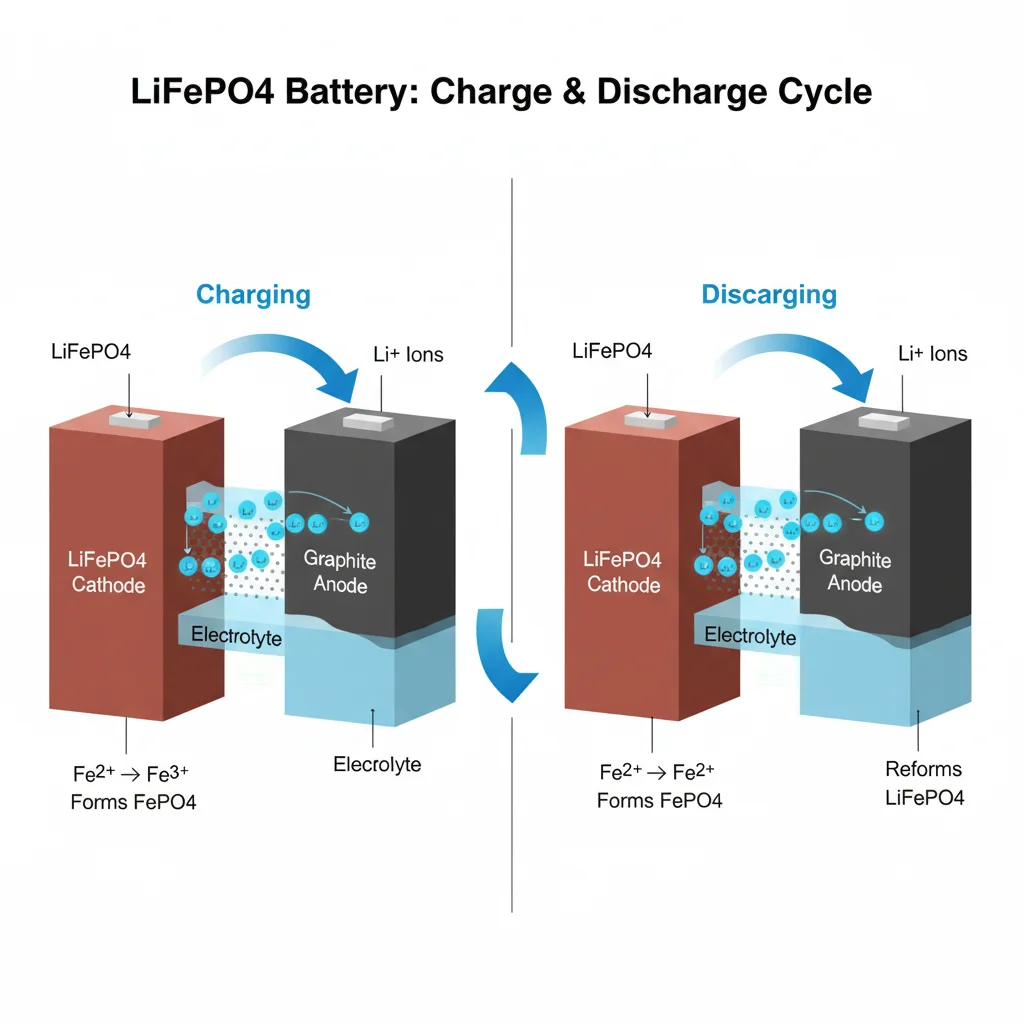
The operational principle of LiFePO4 batteries generally follows that of typical lithium-ion batteries, but with its own unique characteristics and reaction mechanisms.
1. Charging Process * Cathode Reaction: During charging, lithium ions deintercalate from the cathode material (LiFePO4) and move into the electrolyte, then transfer to the anode material. Simultaneously, ferric ions (Fe3+) in the cathode material are oxidized to ferrous ions (Fe2+), forming FePO4. * Anode Reaction: At the anode (typically graphite), lithium ions combine with carbon material, forming a lithium-carbon compound.
2. Discharging Process * Cathode Reaction: During discharge, lithium ions migrate back from the anode to the cathode, where FePO4 is reduced back to LiFePO4, releasing the stored lithium ions. * Anode Reaction: At the anode, the lithium-carbon compound oxidizes back to carbon, releasing lithium ions which return to the electrolyte.
3. Battery Reactions * Cathode Reaction: LiFePO4 ↔ Li+ + FePO4 * Anode Reaction: C6 ↔ LiC6
4. Overall Principle * The reversible movement of lithium ions between the cathode and anode facilitates the charging and discharging processes. * Lithium ion transfer and chemical reactions between the electrode materials during charge and discharge result in the battery's performance characteristics.
3. Pros and Cons
Advantages
- High Safety: Due to their stable structure, LFP batteries are less prone to overheating, combustion, and other safety issues, making them more reliable than other lithium battery types.
- Long Cycle Life: Typical LFP batteries can achieve thousands of charge-discharge cycles, offering a long service life suitable for stable, long-term operation.
- Fast Charging Capability: LFP batteries generally exhibit good fast-charging performance, allowing them to be charged quickly while maintaining stable performance.
- Environmentally Friendly: They do not contain heavy metals or rare earth materials, making them environmentally friendly and recyclable.
- Strong Stability: They perform well under high temperatures, overcharging, and over-discharging conditions, and are less likely to experience thermal runaway or damage.
Disadvantages
- Relatively Lower Energy Density: Compared to other lithium batteries, LFP batteries have a relatively lower energy density, meaning they might require more volume or weight to store the same amount of energy.
- Higher Cost (Historically): Manufacturing processes can be complex, leading to a relatively higher production cost, which historically impacted their competitiveness (though this gap is closing).
- Higher Self-Discharge Rate: Compared to some other lithium battery types, LFP batteries can have a slightly higher self-discharge rate, potentially leading to more energy loss over time when not in use.
- Poorer Low-Temperature Performance: In extremely cold environments, the performance of LFP batteries may be affected, leading to reduced discharge efficiency.
LiFePO4 batteries hold a significant position across many applications thanks to their high safety, long lifespan, and eco-friendly characteristics. However, it's crucial to consider their relatively lower energy density, historical higher cost, and performance limitations under specific conditions. When choosing a battery, you should weigh its pros and cons against your specific needs and application scenarios to achieve the best performance and cost-effectiveness.
4. LiFePO4 Batteries Application Areas
Due to their high safety, long cycle life, and stability, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries are widely used in many fields. Here are common application areas for LFP batteries:
- 1. Electric Vehicles (EVs): LFP batteries are favored as power sources for electric vehicles. Their high safety and long cycle life make them a crucial battery type in the EV industry.
- 2. Energy Storage Systems (ESS): In ESS, LFP batteries are extensively used in home and commercial storage systems for balancing power demand, backup power, and managing peak loads.
- 3. Solar Energy Storage: When paired with solar photovoltaic systems, LFP batteries can store solar energy collected during the day for power supply at night or on cloudy days.
- 4. Power Tools: LFP batteries are widely applied in power tools, electric bicycles, and similar devices, providing reliable power support.
- 5. Communication Base Stations: Due to their long cycle life and stability, LFP batteries are often used as backup power for mobile communication base stations.
- 6. Smart Homes: In the smart home sector, LFP batteries power various smart devices and home appliances, offering stable and reliable energy.
- 7. Medical Equipment: LFP batteries are extensively used in portable medical devices and emergency equipment, ensuring their normal operation.
LFP batteries are widely applied across electric vehicles, energy storage systems, solar energy storage, communication base stations, and more, thanks to their superior performance and safety.
5. Considerations When Choosing LiFePO4 Batteries
When selecting and using Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries, several key considerations are important to ensure optimal performance and safety. Here are aspects to keep in mind:
- 1. Product Quality and Reliability:
- Choose reputable and well-known manufacturers to ensure products meet relevant standards and certification requirements.
- Review product quality certifications and test reports to confirm the battery meets desired performance indicators.
- 2. Battery Parameter Matching: Ensure that the selected battery parameters (capacity, voltage, etc.) match the requirements of the application device to prevent performance degradation or damage.
- 3. Charge and Discharge Characteristics: Understand the charge and discharge characteristics of the LFP battery, including charging speed and cycle life, to choose a suitable model based on actual needs.
- 4. Safety Features: Pay attention to the product's safety features, including overcharge protection, over-discharge protection, and over-temperature protection, to prevent accidents during use.
- 5. Operating Environment: Consider the temperature range of the operating environment and select a battery model that can adapt to high or low temperatures, ensuring normal operation under various environmental conditions.
- 6. Cost-Effectiveness: Evaluate factors like price, performance, and lifespan to choose a product with good cost-effectiveness, achieving the best balance.
- 7. After-Sales Service: Consider the after-sales service and technical support provided by the manufacturer to ensure timely assistance and guarantees during use.
When choosing LFP batteries, beyond product quality and performance matching, it's essential to consider safety, operating environment, and cost-effectiveness. By comprehensively evaluating these factors, you can select the right LFP battery for your needs, ensuring proper device operation and extending battery life.
6. Charging Methods for LiFePO4 Batteries
Proper charging methods are crucial for the performance and lifespan of Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries. Here are recommended charging methods and considerations for LFP batteries:
- 1. Conventional Charging:
- Use chargers specifically designed for lithium-ion batteries.
- Set the correct charging voltage and current to match the battery's charging requirements.
- 2. Charging Voltage Range:
- Typically, the charging voltage range for a single LFP cell is 3.6V to 3.65V.
- Avoid exceeding the battery's specified maximum charging voltage to prevent damage.
- 3. Charging Current Control:
- Control the charging current appropriately, not exceeding the battery's specified maximum.
- Avoid using excessively high charging currents to improve charging efficiency and extend battery life.
- 4. Charging Temperature:
- It's advisable to charge at lower ambient temperatures; avoid charging in high-temperature environments.
- Ensure the battery does not overheat during charging, keeping the charging temperature within an appropriate range.
- 5. Full Charge State:
- Stop charging promptly once the battery is full to avoid overcharging, which can damage the battery.
- Over-discharging or over-charging is not recommended, as it shortens battery lifespan.
- 6. Charging Time:
- Do not leave the battery in a charging state for extended periods to prevent overcharging from causing electrolyte decomposition and battery damage.
- 7. Important Notes:
- Always follow the charging guidelines and recommendations provided by the battery manufacturer.
- Do not reverse-charge the battery, as this can lead to safety issues.
Correct charging methods are vital for the performance and longevity of LFP batteries. Following these guidelines helps ensure proper charging, extends battery life, and enhances safety. For specific needs or questions, it's recommended to consult the battery manufacturer or a professional for detailed guidance.
7. LiFePO4 vs. Ternary Lithium Batteries: Which is Better?
Both Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) and Ternary Lithium batteries (typically NMC - Nickel Manganese Cobalt) are important types of lithium-ion batteries, each with distinct advantages and characteristics. Here’s a comparative overview:
Advantages of LiFePO4 Batteries:
- Safety: LFP batteries are more stable under high temperatures, overcharging, and over-discharging conditions, offering higher safety.
- Cycle Life: They boast a long cycle life, achieving thousands of cycles, suitable for long-term stable use scenarios.
- Environmentally Friendly: Do not contain heavy metals or rare earth materials, making them environmentally friendly.
- Fast Charging Capability: Possess good fast-charging performance.
Disadvantages of LiFePO4 Batteries:
- Lower Energy Density: Compared to Ternary Lithium batteries, LFP batteries have a lower energy density.
- Higher Cost (Historically): Production costs were relatively higher (though this is rapidly changing).
- Higher Self-Discharge Rate: They can have a slightly higher self-discharge rate compared to some other battery types.
Advantages of Ternary Lithium Batteries (NMC):
- High Energy Density: Ternary Lithium batteries offer higher energy density, making them lighter and more compact for the same energy storage.
- Faster Charging Speed: Exhibit good fast-charging performance, suitable for applications requiring frequent charging and discharging.
- Better Temperature Adaptability: Tend to perform better in extreme temperature environments.
Disadvantages of Ternary Lithium Batteries (NMC):
- Safety: Safety is generally considered slightly inferior compared to LFP batteries, particularly regarding thermal runaway.
- Cycle Life: Cycle life is typically somewhat shorter than that of LFP batteries.
- Cost: Manufacturing costs can be relatively high (though also subject to market fluctuations).
Choosing between LFP and Ternary Lithium batteries depends on specific application requirements. If high safety and long cycle life are paramount, LFP batteries might be a better fit. If high energy density and fast charging performance are the primary goals, Ternary Lithium batteries might be more suitable. When making a choice, it's essential to weigh these factors comprehensively against the specific application scenario.
Backed by 12 years of expertise in the new energy sector, Guangdong Elecno Technology Development Co., Ltd. is a premier manufacturer of lithium battery products, including household/industrial energy storage LiFePO4 batteries, UPS, and outdoor power. Located in Dongguan, China, with a Zhengzhou branch, our 27,000+ sqm factory operates with multiple automated lines. Certified with CE, RoHS, ISO9001, and more, Elecno prioritizes high specific capacity, reliability, and safety across its innovative product range.





